Magnetism and Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism
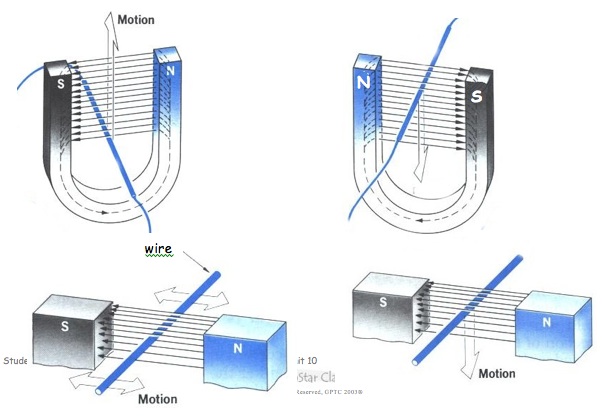
 The magnetic field created by a solenoid is similar to the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The right hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a wire. When a bar magnet moves into a coil of wire a current is induced. This process is called electromagnetic induction. You will learn about these concepts in this lesson.
The magnetic field created by a solenoid is similar to the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The right hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a wire. When a bar magnet moves into a coil of wire a current is induced. This process is called electromagnetic induction. You will learn about these concepts in this lesson.
Guiding Questions
|

|
- How can you determine the direction of a magnetic field in a current carrying wire?
- How do you apply the right hand rule to straight wires and solenoids?
- How does an electromagnet work?
- What factors affect the strength of an electromagnet?
- How does electromagnetic induction work?
- How are motors and generators different?
|
Key Terms
- Alternating current- A current that changes direction at regular intervals.
- Direct current- A current that flows in the same direction.
- Electric motor- A machine that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
- Electromagnet- A temporary magnet whose magnetic field is produced by an electric current.
- Electromagnetic induction- The process of creating a current or voltage in a circuit loop by moving a conductor through a magnetic field.
- Generator- A machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Right hand rule- A useful way to visualize the direction of a magnetic force.
- Solenoid- A long, helically wound coil of insulated wire.
- Transformer- A device that increases or decreases the voltage or alternating current.
Standards
RST 11-12.3: Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks; analyze the specific results based on explanations in the text.
RST 11-12.4: Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 11-12 texts and topics.
RST 11-12. 7: Integrate and evaluate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media in order to address a question or solve a problem.
WS 11-12.2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas, concepts and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content.
Watch
|

|
Before watching this video, please download the study guide to fill out as you watch the video. You may pause the video if you need to do so. There is also a video script which you may also download for a text version of this information. The information found in the study guide will be useful to help you prepare for the quizzes and exams.
Watch this to learn about Electromagnetism. The video is approximately 30 minutes long.
(Media may take time to load; please be patient.)
Bright Cove: Electromagnetism (29:12 min)
|
Video Source: http://link.brightcove.com/services/player/bcpid9113583001?bctid=1406589027
If you have trouble loading the above video try watching it in segments
- Introduction
- Discovery of Electromagnetism
- Prelab Part A
- Lab Part A
- Lab Part B
- Electromagnets
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Electric Generators
- Lenz's Law
- Electric Motors and Review
Electromagnetism Practice
Use the following practice activity to assess what you have learned from the video.
Use the rule (shown in two versions) to answer the following questions:
1. In the diagrams below, a compass is placed above or beneath each wire. Draw a large arrow to the side, showing the direction of the current. Then draw the compass needles, showing the direction they point.
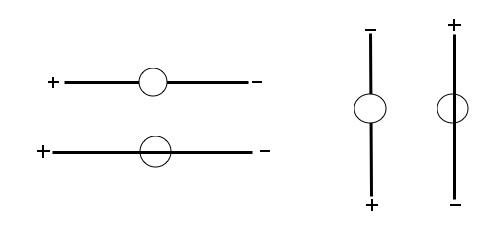
2. This cross-section view of a wire shows the current moving (out of) the page. Draw arrows showing the direction of the magnetic field around the wire.

3. This cross-section view of a wire shows the current moving (into) the page. Draw arrows showing the direction of the
magnetic field around the wire.

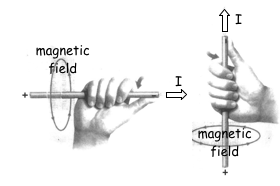
Right-Hand Rule #2:
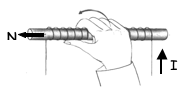
1. The linear coil of conducting wire is called a ___________.
2. When a soft iron core is placed inside the wire, an ___________ is created. To increase the strength of this magnet, you can increase _________________ and increase ________________.
Right-Hand Rule #3 (the generator rule):
1. Use your notes to show what each arrow represents. (This will be given to you on a test.)
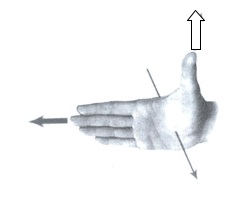
2. In each case below, use the right-hand rule above to determine the direction the current will flow. Draw an arrow on the wire to show the direction of the current. Draw an "X" if no current will flow.
Electromagnetism Animation: Magnetic Field Lines of a Straight Current-Carrying Wire
Electromagnetism Animation: Electric Generator
Handouts
Electromagnetism Lab
Transformers Virtual Lab
Electromagnet Hands On Lab
Handouts
Electromagnetism Lab - Electromagnetism_Lab_MagnetismandElectromagnetism.doc
Transformers Virtual Lab - Transformers_Worksheet_MagnetismandElectromagnetism.doc
Electromagnet Hands On Lab - Electromagnet_Hands_On_Lab_MagnetismandElectromagnetism.doc
 The magnetic field created by a solenoid is similar to the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The right hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a wire. When a bar magnet moves into a coil of wire a current is induced. This process is called electromagnetic induction. You will learn about these concepts in this lesson.
The magnetic field created by a solenoid is similar to the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The right hand rule can be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a wire. When a bar magnet moves into a coil of wire a current is induced. This process is called electromagnetic induction. You will learn about these concepts in this lesson.






